Hey there! If you’ve ever wondered about your Body Mass Index (BMI) and how to calculate it, you’re in the right place. Understanding BMI can be a game-changer for your health journey. It’s a simple way to gauge whether you’re in the healthy weight range for your height. Let’s dive into what BMI is, how it works, and how you can calculate yours. Ready? Let’s go! The Interesting Info about bmi calculator.
Definition of BMI
BMI, or Body Mass Index, is a number calculated from your weight and height. It provides a quick assessment of your body composition by estimating the amount of body fat you might have. While it isn’t a direct measure of body fat, it uses your height and weight to offer a rough estimate.
Historical Context
The concept of BMI was first developed in the early 19th century by Adolphe Quetelet, a Belgian mathematician. Quetelet’s formula, known as the Quetelet Index, was designed to offer a simple way to categorize individuals based on weight and height. This simplicity has made BMI a staple in health assessments worldwide.
How BMI Works
Think of BMI as a quick snapshot of your body composition. Although it doesn’t measure body fat directly, it correlates with more direct measures of body fat, making it a handy tool for health professionals. BMI is often used in conjunction with other diagnostic tools to provide a comprehensive view of an individual’s health.
Why Is BMI Important?
Health Assessment Tool
You might be thinking, “Why should I care about BMI?” Well, understanding your BMI can help you and your healthcare provider determine if you’re at a healthy weight, underweight, overweight, or obese. These categories can help assess your risk for health issues like heart disease, diabetes, and more.
Risk Indicator
A high BMI is often associated with an increased risk of certain health conditions. For example, a BMI in the overweight or obese range can indicate a higher risk for developing type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular diseases. Recognizing these risks early allows individuals to take preventive measures to improve their health.
Public Health Implications
On a larger scale, BMI is used by public health officials to monitor population health trends. It provides valuable data that can inform health policies and initiatives aimed at reducing obesity rates and improving overall public health outcomes.
How to Calculate Your BMI
The Formula
Calculating your BMI is super simple. You don’t need to be a math whiz to figure it out! Here’s the formula:
Metric Measurements
For metric measurements:[ \text{BMI} = \frac{\text{weight in kilograms}}{(\text{height in meters})^2} ]
This formula uses kilograms for weight and meters for height, which are standard units in most countries.
Imperial Measurements
For imperial measurements:[ \text{BMI} = \frac{\text{weight in pounds} \times 703}{(\text{height in inches})^2} ]
The imperial formula is commonly used in the United States, where weight is often measured in pounds and height in inches.
Step-by-Step Guide
Let’s break it down step-by-step so you can easily calculate your BMI at home.
Measuring Height and Weight
Measure Your Height and Weight: Use a reliable scale for your weight and a tape measure for your height. Make sure you’re using the correct units for your preferred formula. Accurate measurements are crucial for calculating an accurate BMI.
Plugging Numbers into the Formula
Plug the Numbers into the Formula: For metric: If you weigh 68 kg and are 1.75 meters tall, your BMI would be: [ \text{BMI} = \frac{68}{(1.75)^2} = 22.2 ] For imperial: If you weigh 150 lbs and are 65 inches tall, your BMI would be: [ \text{BMI} = \frac{150 \times 703}{65^2} = 24.96 ] This step is straightforward and quick once you have your measurements.
Interpreting the Results
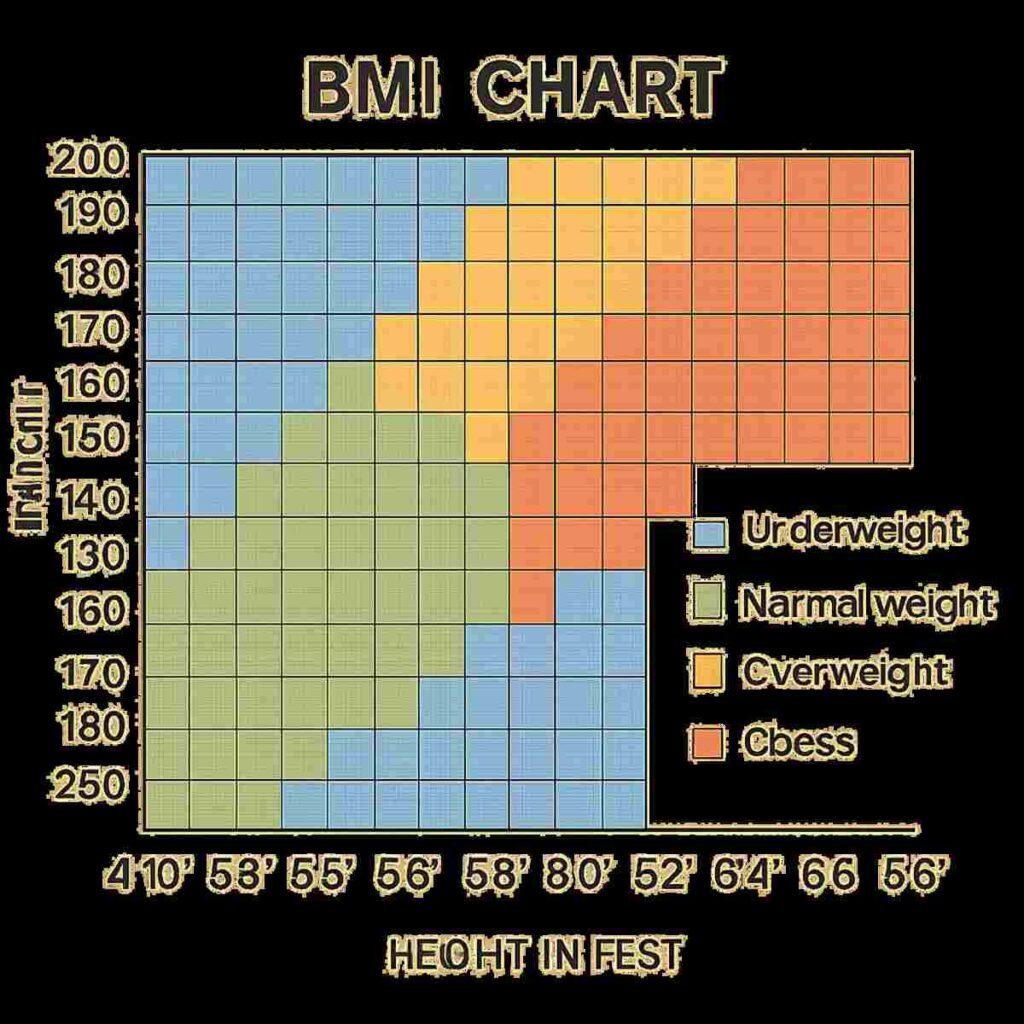
Interpret the Results: Use a BMI chart to determine which category you fall into. This will help you understand whether you are in the underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese category and what that means for your health.
BMI Categories
Underweight
Here’s how the BMI categories typically break down:
Underweight: BMI less than 18.5 Being underweight can indicate malnutrition, a high metabolism, or underlying health issues. It’s important for those in this category to consult with healthcare providers to ensure they are getting adequate nutrition.
Normal Weight
Normal weight: BMI 18.5-24.9 A normal BMI suggests that you are within a healthy weight range for your height. Maintaining a balanced diet and regular physical activity can help keep you in this range.
Overweight and Obesity
- Overweight: BMI 25-29.9
- Obesity: BMI 30 or higher Both categories indicate a higher than normal body fat percentage, which can increase the risk of various health conditions. Individuals in these categories should consider lifestyle changes and consult with healthcare professionals for guidance.
Limitations of BMI
Muscle vs. Fat
While BMI is a useful tool, it’s not without its flaws. It doesn’t distinguish between weight from fat and weight from muscle. So, someone very muscular might have a high BMI but not have excess body fat. This limitation can lead to misclassification, especially in athletes or individuals with high muscle mass.
Variability Among Individuals
Likewise, it doesn’t account for differences in muscle mass, bone density, and overall body composition, which can vary significantly among individuals. Therefore, it’s always good to use BMI as just one of several measures to assess your health.
Ethnic and Age Considerations
Different populations may have different body compositions, which can influence BMI readings. Additionally, as people age, their muscle mass tends to decrease, which can affect BMI accuracy. It’s important to consider these factors when interpreting BMI.
BMI for Women
General Application
When it comes to using a BMI calculator specifically for women, it’s important to remember that the categories apply similarly to both men and women. However, women generally have more body fat than men, so it’s crucial to consider other factors like waist circumference and overall body composition for a fuller picture.
Hormonal Influences
Women experience hormonal changes throughout their lives, such as during menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause, which can affect body composition and weight distribution. These factors can influence BMI and should be considered when assessing health.
Additional Health Indicators
For a comprehensive health assessment, women should also consider other indicators such as body fat percentage, waist-to-hip ratio, and overall fitness level. These measures can provide a more detailed understanding of health beyond BMI alone.
Tools to Track Your BMI
Online Calculators
There are many online BMI calculators that can do the math for you. Just input your height and weight, and voila! You’ve got your BMI. These tools are convenient and can provide instant results without manual calculations.
Mobile Apps
Some apps even track your BMI over time, which can be super helpful if you’re on a weight loss or fitness journey. These apps often include additional features like goal setting, progress tracking, and personalized health tips.
Wearable Technology
Wearable devices, like fitness trackers and smartwatches, can also help you monitor your BMI and other health metrics. These devices often sync with mobile apps to provide comprehensive health insights and trends over time.
Real-World Applications
Setting Health Goals
Understanding your BMI can help you set realistic health goals. For instance, if your BMI falls into the overweight category, you might decide to adopt healthier eating habits or increase your physical activity to bring that number down. Setting achievable goals is key to long-term success.
Monitoring Progress
Regularly checking your BMI can provide motivation and track your progress towards health goals. It serves as a tangible measure of success and can be a useful tool for staying accountable.
Health Consultations
Discussing your BMI with healthcare professionals can lead to personalized advice and interventions. They can help interpret your BMI in the context of other health indicators and develop a tailored plan for improving or maintaining your health.
Practical Tips and Exercises
Track Your Progress
Track Your Progress: Regularly check your BMI to see how lifestyle changes are affecting your weight. Keeping a log can help identify trends and areas for improvement.
Balanced Diet
Balanced Diet: Aim for a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. A nutritious diet supports weight management and overall health.
Stay Active
Stay Active: Incorporate regular exercise into your routine. Even a daily walk can make a big difference! Consistent physical activity improves cardiovascular health, builds muscle, and helps maintain a healthy weight.
Conclusion
Calculating and understanding your BMI is a simple yet effective way to monitor your health. While it’s not a perfect measure, it offers valuable insights into your weight category and potential health risks. Remember, it’s just one tool in your health toolkit. Always consider other factors and consult with healthcare professionals for a comprehensive view of your health.
Thanks for sticking around! Now that you’ve got the hang of it, why not try calculating your BMI and see where you stand? Here’s to a healthier you!